Natural Gas Deregulation
This oil crisis would have a huge impact on the natural gas industry and eventually lead to the deregulation of natural gas. Desiring more affordable energy than electricity or petroleum, energy consumers turned en masse to natural gas. For those unaware, natural gas is a source of energy from fossil fuels that has been used for heat for hundreds of years and was eventually used to generate electricity. This sudden shift caused significant shortages in natural gas markets across the country.
Eventually, the Natural Gas Policy Act of 1978 was introduced to combat these shortages. The act removed federal price regulations that had prevented the industry from expanding and innovating while it consolidated smaller, local gas markets to achieve economies of scale. This change motivated industry players to improve their infrastructure and production methods and helped balance the natural gas supply with its increased demand.
This partial deregulation of natural gas rates helped to lessen the strain on the market and propel the country’s natural gas technology and policies forward in a big way.
The Final Restructuring Rule
The Final Restructuring Rule, formally known as FERC Order No. 636, was a 1992 order that required natural gas pipelines – who had traditionally charged customers for producing, transmitting, and distributing natural gas – to unbundle their services and allow consumers to choose their suppliers. Because of this order, business owners who live in states deregulated for natural gas can shop for their own natural gas suppliers to provide their business energy.
Several other necessary orders and policies, including the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission's (FERC) Order No. 436 and the Natural Gas Wellhead Decontrol Act, helpedwould further set the stage for natural gas deregulation at the federal level.
Electricity Deregulation
Just like natural gas deregulation, electricity deregulation refers to the system in which there is an open market for the supplying and purchasing of electricity in an effort to avoid utility monopolies and lower costs for the consumer.
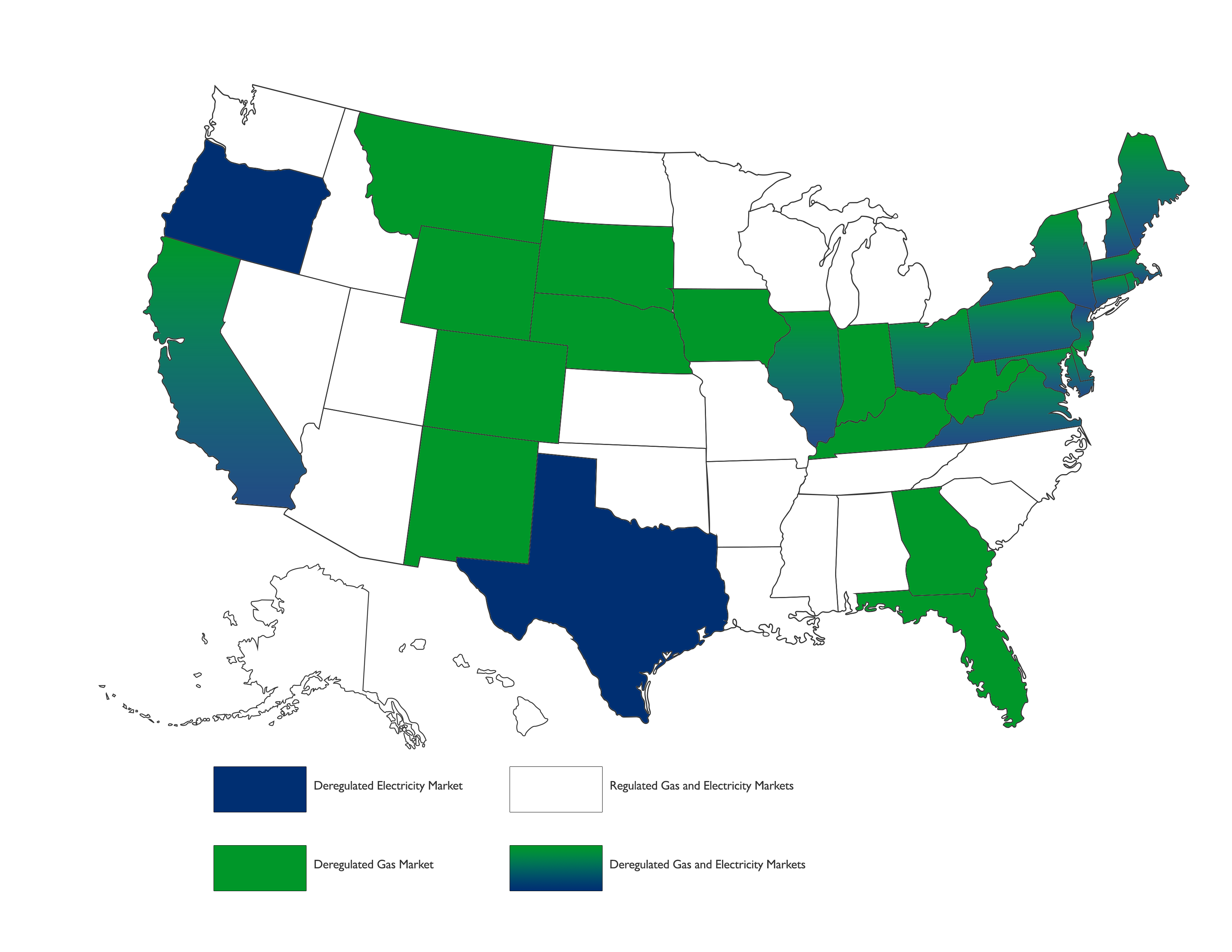
How Many States Are Deregulated for Energy?
![Energy US map]()
Currently, 30 states are deregulated for energy at some level. Fourteen states are deregulated for both electricity and natural gas, 21 states are deregulated for just electricity, and 24 states are deregulated for just natural gas. Deregulated states include:
How Do Deregulated Markets Work?
People living and working in deregulated energy and electricity markets have the right to select the energy company for their home or business, allowing them to essentially shop for the best energy prices. Deregulated markets work like a reverse auction, with energy providers competing to offer the lowest rate. Independent companies purchase this bulk energy based on careful predicted use calculations. Based on the expected supply-demand algorithm, they then provide their customers with the most competitive rate possible.
This energy is transported to homes or businesses through local utility companies. In regulated markets, consumers must use whatever supplier the utility defaults to without the option of shopping the rates offered by independent suppliers. While this makes the selection and set up process more straightforward, it allows for the monopolization of energy in that particular area.
How Does Energy Deregulation Impact My Business?
Because energy deregulation puts the power of choice into the consumers’ hands, suppliers must win over their customers. In both deregulated natural gas and deregulated electricity markets, the rivalry among suppliers can lead them to offer more competitive pricing and improved energy technologies (including renewable technologies) to earn the business of energy shoppers, including business owners.
Additional benefits of deregulation include:
- Lower Rates: A large number of suppliers means increased competition in the deregulated market, which drives down business energy rates.
- Custom Billing Solutions: Flexibility in pricing and billing structure is another benefit of deregulated energy. Many suppliers offer unique or customizable pricing plans to stand out in a competitive market.
- Enhanced Customer Service: Pricing isn’t the only point of competition for energy suppliers. Customer service increasingly sets energy suppliers apart from the competition, and consumers in deregulated markets enjoy premium service and sophisticated consumer platforms.
- Greener Energy Options: Suppliers recognize that consumers want environmentally friendly energy options. Many business owners are looking to go green with alternative energy sources. The deregulated market allows consumers to select an alternative energy option like wind or solar power, helping them implement or create environmental goals for their business or industry.
![Green energy options]()
Renewable Resources and the Deregulated Market
A competitive energy market also benefits businesses seeking renewable business energy sources. According to Energy.gov, approximately 20% of all energy in the United States is powered by renewable sources, with wind power being the most common renewable source of energy. Suppliers seek better, cleaner, and more sustainable energy sources to meet the growing consumer demand for environmentally conscious energy. Consumers are increasingly likely to consider a business’s clean energy efforts and environmental footprint when purchasing.
Integrity Energy is Here to Help!
To best leverage the advantages of the deregulated energy market for your business, it is imperative to shop around for the best energy rate. At Integrity Energy, we recognize that few business owners have the time or inclination to learn the complicated and ever-changing nuances of the deregulated market, and that’s okay because our energy experts are standing by to partner with you as you navigate the shopping process! It’s our goal to connect you with the best, most cost-efficient suppliers so you can focus on operating and growing your business.